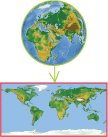
Distortion in geography refers to the alteration of the shape, size, or distance of geographic features on maps compared to the actual Earth’s surface. It’s a crucial concept to understand when interpreting maps and spatial relationships. Distortion can result from the challenge of representing a three-dimensional, spherical Earth on a two-dimensional map accurately. Let’s delve deeper into what does distortion mean in geography and how it impacts our perception of the world around us.
Understanding Distortion in Geography
Welcome to our exploration of what distortion means in geography! Have you ever looked at a map and wondered why some countries appear larger or smaller than they actually are? That’s where distortion comes into play. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of map projections and how they can impact our understanding of the world around us.
What is Distortion?
Distortion in geography refers to the misrepresentation of the size, shape, distance, or direction of geographic features on a map compared to their actual measurements on the Earth’s surface. It occurs because it is impossible to accurately represent the three-dimensional surface of the Earth on a two-dimensional map without some form of distortion.
Types of Distortion
There are several types of distortion that can occur in maps, including:
- Shape Distortion: When the shapes of countries or landmasses are altered on a map.
- Size Distortion: When the relative sizes of countries or landmasses are misrepresented.
- Distance Distortion: When the distances between points on a map are not accurate.
- Direction Distortion: When the compass directions on a map are not true to reality.
Causes of Distortion
Distortion in maps can be caused by the way the Earth’s surface is projected onto a flat map. There are different map projections, each with its own way of representing the Earth’s surface, and each projection inevitably introduces some form of distortion.
Map Projections
Map projections are methods used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map. Some common map projections include the Mercator projection, the Peters projection, and the Robinson projection. Each projection has its strengths and weaknesses, leading to different types and degrees of distortion.
Mercator Projection
The Mercator projection is one of the most well-known map projections. It is a cylindrical projection that preserves angles and shapes but distorts sizes, especially near the poles. This is why countries near the equator appear smaller than they actually are, while countries near the poles appear larger.
Peters Projection
The Peters projection, also known as the Gall-Peters projection, was created to address size distortion issues in the Mercator projection. It accurately represents the relative sizes of countries and landmasses but distorts shapes, particularly near the equator.
Robinson Projection
The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that attempts to balance distortions in shape, size, distance, and direction. It is commonly used in world maps because it provides a visually appealing representation of the world with minimal distortion.
Implications of Distortion
Distortion in maps can have significant implications for how we perceive the world around us. For example, size distortion can lead to misconceptions about the true sizes of countries, while shape distortion can alter our understanding of geographic boundaries. Understanding the types of distortion in maps is crucial for interpreting geographical information accurately.
Educational Applications
Distortion in geography is not just a theoretical concept—it has practical implications in education. Teachers often use discussions about map distortion to teach students about the limitations of maps and the importance of critical thinking when analyzing geographic information. By understanding how distortion can affect maps, students can develop a more nuanced understanding of the world.
Global Perspective
On a global scale, distortion in maps can influence political discussions, trade agreements, and international relations. Maps play a crucial role in shaping our perception of the world, and being aware of how distortion can impact these perceptions is essential for making informed decisions.
In conclusion, distortion in geography is a complex but essential concept to understand when interpreting maps. By recognizing the types of distortion that can occur and the factors that contribute to it, we can develop a more informed perspective on the world around us. Next time you look at a map, remember that what you see may not always be an accurate representation of reality due to distortion!
Mercator projection
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes distortion in geography maps?
Distortion in geography maps is primarily caused by the challenge of representing a three-dimensional spherical Earth on a two-dimensional flat surface. This distortion occurs due to the projection method used to convert the globe onto a map, leading to inaccuracies in shapes, areas, distances, or directions.
How does distortion affect map interpretation?
Distortion impacts map interpretation by altering the relative size and shape of landmasses, bodies of water, and other features. This can misrepresent the actual spatial relationships between locations, leading to errors in navigation, planning, and analysis based on the map.
Are there ways to minimize distortion in geography maps?
Yes, cartographers use different map projections to minimize specific types of distortion depending on the map’s purpose. For example, equal-area projections preserve the correct sizes of areas but may distort shapes, while conformal projections maintain accurate shapes but can distort sizes. Choosing an appropriate projection is crucial to reducing distortion in maps.
How can one identify distortion in a geography map?
Distortion in a geography map can be identified by comparing it to alternative projections or reference maps. Look for disparities in the size and shape of countries or continents, as well as the distortion of meridians and parallels. Analyzing how grid lines, scales, and distances appear on the map can also reveal the extent of distortion present.
Final Thoughts
Distortion in geography refers to the misrepresentation of the Earth’s surface on maps due to the challenge of projecting a three-dimensional object onto a two-dimensional plane. This results in inaccuracies in size, shape, distance, or direction. Understanding the different types of map projections helps geographers to interpret and analyze spatial information effectively. In conclusion, grasping what distortion means in geography is crucial for map users to interpret geographical data accurately. Efficiently managing and minimizing distortion can lead to more precise and reliable spatial analysis.